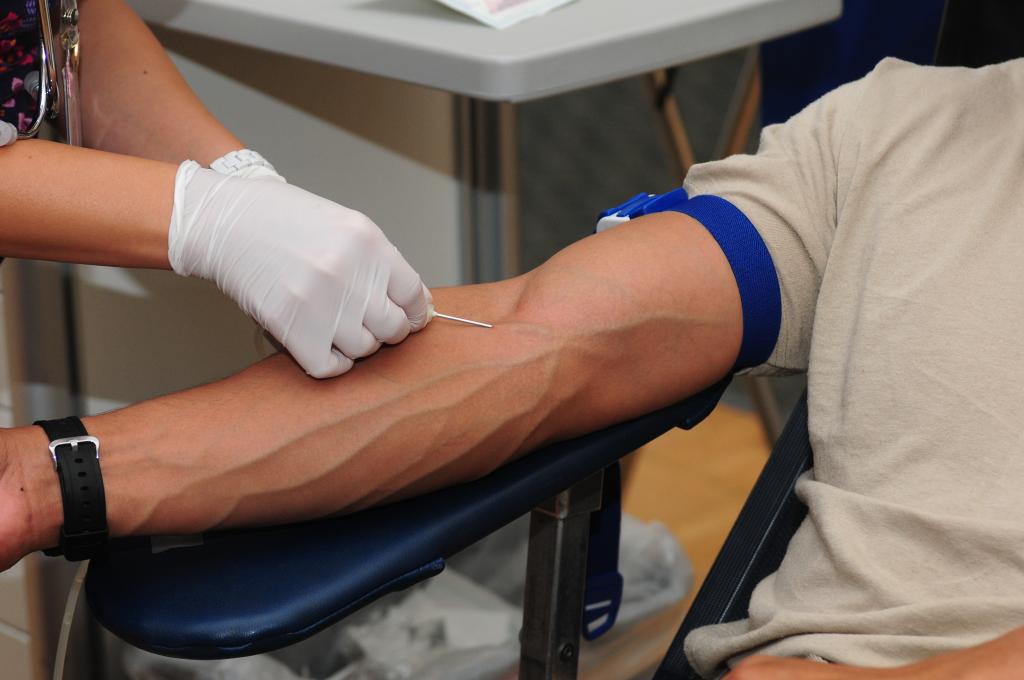
When you donate two units of blood, do you know what it entails? “Double red cell donation” refers to the practice of donating solely red blood cells as opposed to the entire blood volume. Everything else in your blood is returned to you, but just the red blood cells are taken out.
- What Is Apheresis Blood Donation? Everything You Need To Know
- How To Make An Anonymous Donation? Ultimate Guide
- What Are The Benefits Of Organ Donation? 9 Things to Consider
- How Much Does Egg Donation Pay? Everything You Need To Know
- How To Start A Donation Fund For Someone With Cancer? Comprehensive Guide
Erythrocytes, or red blood cells, transport oxygen, water, vitamins, and minerals to every cell in the body. While white blood cells carry oxygen around the body, red blood cells are responsible for returning waste products like carbon dioxide to the lungs.
Bạn đang xem: What Is Double Red Cell Donation? Everything You Need To Know
Double red cell donation refers to the process of donating two units of red blood cells during a single session. Unlike whole blood donation, which benefits only one person, this procedure saves the lives of two. You may learn a lot more about this topic if you read up on it.
What is a Double Red Donation?
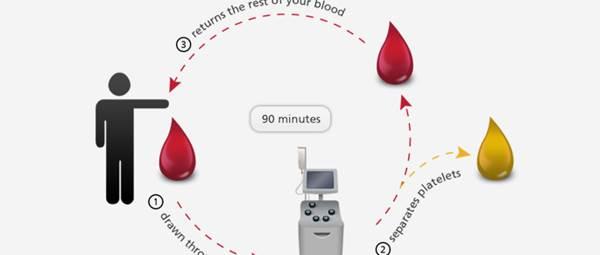
In a double red cell donation, the red cells are separated from the donor’s blood using a specific apparatus, allowing them to donate twice as many red blood cells in a single visit. The donor receives the plasma, platelets, and other blood components.

Double red cell donor requirements
Donating twice as many red blood cells in one sitting is made possible through double red cell donation, which involves separating the red cells from the blood using specialized equipment. Plasma, platelets, and other blood components are returned to the donor.
- No one under the age of 17 can be a donor.
- Donating blood requires that the patient has a certain level of iron in their blood.
- There are size requirements for donors.
- In order to give twice in the color red, donors must schedule an appointment in advance.
Type O donors are ideal for double red cell contributions because they account for 45% of the population. There is an increased demand for Type O Negative blood now that it is possible to give it to all patients.
What Sickness Can You Acquire That Relates To RBCs?
There is no way to overstate the significance of red blood cells in the human body. If red blood cell counts (RBCs) drop too low, a person’s life could be at jeopardy. Consider how ill we may get if our RBC count dropped and the value of a double red cell transfusion.
#1. Anemia
Anemia is characterized by a blood count that is abnormally low in red blood cells. The afflicted cells are the red blood cells. A lack of the mineral iron in our blood is a contributing factor. Iron deficiency anemia, the most prevalent type of anemia, develops when the body does not have enough iron to properly function.
#2. Thalassemia
Xem thêm : How Much Do I Get Paid For Sperm Donation? Perfect Information For You!
Thalassemia describes a category of inherited blood illnesses. Several diseases can be brought on by disruptions in the normal synthesis of hemoglobin due to genetic defects. Due to this, the body’s organs become dysfunctional and useless. Thalassemia can cause an enlarged spleen, bone abnormalities, and delayed growth in children.
#3. Polycythemia vera
It’s common knowledge that high levels of certain proteins in the blood can lead to strokes and heart attacks, but did you realize that too many red blood cells can cause these problems as well? Having an excessive number of red blood cells is, in fact, harmful. In people with Polycythemia Vera, the bone marrow overproduces red blood cells.
How Does Double Red Cell Donation Work?
It’s common knowledge that too many red blood cells can lead to a stroke or heart attack, but did you know that? An unhealthy level of red blood cell count is actually detrimental. The bone marrow of persons with Polycythemia Vera produces an abnormally large number of red blood cells.
What Are The Drawbacks In Donating?
Donating two units of red blood cells twice had no long-term negative consequences on recipients. Donors often receive saline solution or volume replacement to make up for fluid losses. Some donors report feeling sick or experiencing pain at the injection site after giving blood.
Do Blood Types Matter When Donating?
Maintaining a steady supply of blood in the blood banks requires donations of all blood types. Most transfusions and needs involve blood types O, A-negative, and B-negative. With these, we can better meet the rising demand for blood at our hospitals.

Even if you don’t intend to donate blood, it’s still important to know what type you are. Knowing such fundamentals can be important, since one never knows when they will come across someone in need of blood and be the only match.
How To Increase Blood Cell Count?
Now that we know how critical it is to maintain a healthy level of red blood cells, let’s investigate which foods are known to do so. However, those who suffer from Polycythemia Vera should not use this technique. Red meat, dried fruits, green leafy vegetables, beans, egg yolks, and organ meats like livers are all we need to eat to receive the iron we need. By increasing the production of robust RBCs, dietary supplements containing folate and vitamin B-12 can be helpful.
Where Can I Donate Double Red Blood Cells?
Since we’re keen on acquiring double red cell donations, we’ll also inquire as to where you can donate your own. Our community’s blood banks are the primary locations for blood donations. There should be enough time to run a few tests in about 30 minutes. Blood donations are also welcomed by medical facilities.
FAQs
What is double red blood cell donation?
Xem thêm : How Do They Take Your Eggs For Donation? Helpful Information!
During a double red cell donation, machines are used to collect the complete blood volume. The plasma is returned to the donor while the RBCs are stored. This gift, which is double the volume of a typical whole blood donation, involves the safe removal of red cells. The abbreviation for “double red blood cell donation,” or DRBC, describes this process.
What are red blood cells used for?
In addition to delivering oxygen and nutrients to the cells, red blood cells also eliminate carbon dioxide and waste from the circulation. Red blood cells are required in the majority of transfusions (more than 70%). Transfusions of red blood cells are necessary for patients who have lost or are at risk of losing large amounts of blood. Patients in this category may be undergoing major reconstructive surgery, have suffered catastrophic injuries, or have a perforated bleeding ulcer.
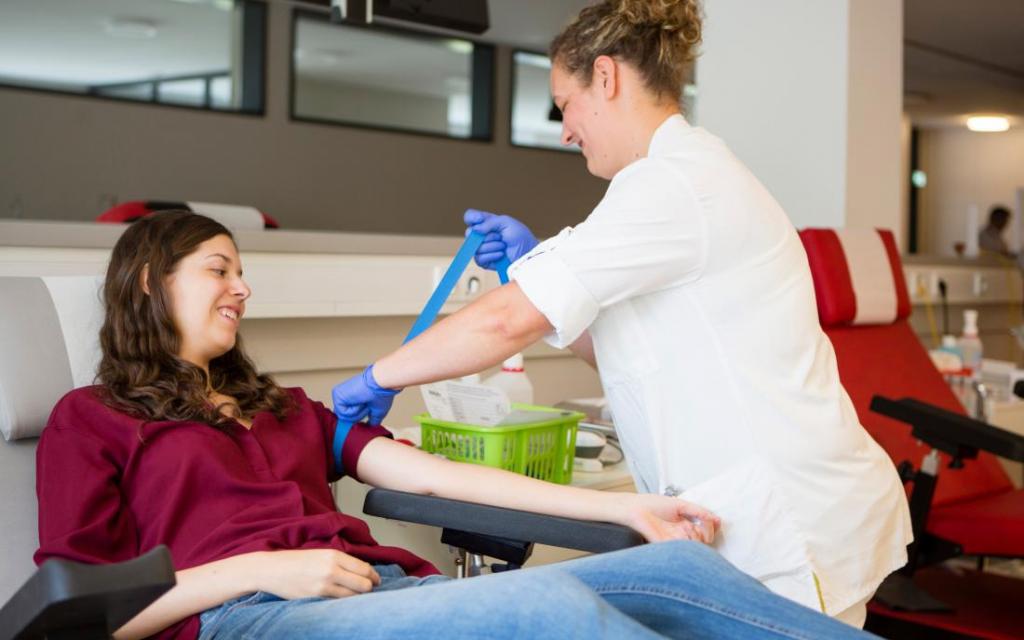
How long does donating take?
Red blood cells are responsible for transporting oxygen and nutrients to cells, as well as removing waste products and carbon dioxide from the bloodstream. In most transfusions, red blood cells are needed (more than 70 percent ). Patients with severe blood loss or at danger of severe blood loss require transfusions of red blood cells. Patients in this category may be undergoing extensive surgery at the present, have suffered serious injuries, or have a perforated bleeding ulcer.
Where can I donate?
Donations of DRBC can be made at any of the three permanent facilities in Campbell, Mountain View, or Menlo Park, or at any of the indoor mobile blood drives held there.
How often can I donate?
Donors aged 16 to 18 are permitted to give blood once a year (365 days). Donating to the DRBC requires that you be 19 or older.
How do I make an appointment to donate?
To schedule a time to give to the DRBC, please call 650-723-7831.
It’s A Wrap!
We now have a better understanding of double red cell donation. Giving blood is like giving someone a second chance at life, and it saves lives in the process. Others could be compelled to give because of how much the world needs a hero like you. Check out these resources to learn more about blood donation and the reasons why my donation was declined:
Gifts in the designated hue will be multiplied by two.
Providing twice as many red blood cells as usual (DRBC)
Nguồn: https://spasifikmag.com
Danh mục: Health