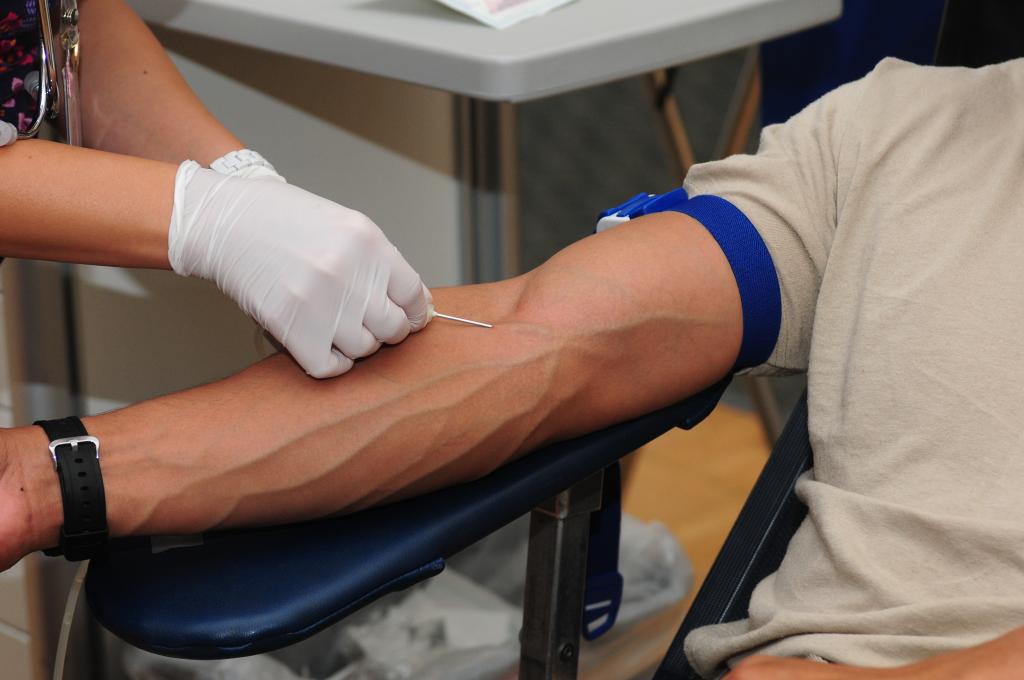
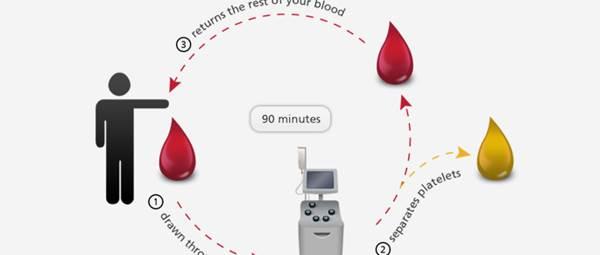
Just what does the act of apheresis donation entail? This novel method of blood collection yields plasma in addition to leukocytes and platelets. The donor’s whole blood supply is separated using a cell separator. The components of blood are separated by spinning the blood in a centrifuge.
The next step is to compile the required quantity of parts and place them in a designated bag. Next, the recipient’s body sends the remaining components and red blood cells back to the donor.
Bạn đang xem: What Is Apheresis Donation? A Helpful Guide
If you compare the amount of platelets donated to a single gift of whole blood, you’ll find that it’s about the same. One platelet transfusion is less likely to provoke an immunological response than many transfusions.
A platelet transfusion from a single donor can help patients whose immune systems are compromised. The majority of them are successful cancer and bone marrow transplant survivors.
What is apheresis?
Apheresis is used to separate blood components such platelets, red blood cells (RBCs), and plasma. By using platelet donations, we can extract only the amount of blood that is necessary for a patient and return the rest to the donor, preventing unnecessary waste.
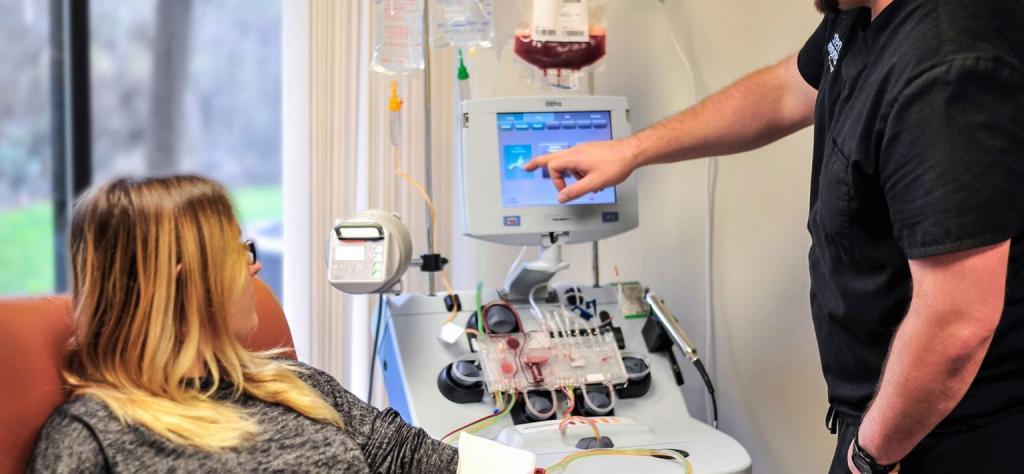
The presence of platelets is essential for blood clotting. Platelet transfusions are occasionally necessary for patients with bleeding issues or those undergoing cancer treatment, open heart surgery, or organ transplantation. Platelets can only be stored for five days after collection, thus they need to be used quickly. The hospital’s supplies will need to be regularly renewed in order to meet this demand. Platelet donations can be made up to a maximum of 24 times per year.
Red blood cells (RBCs) are vital for oxygen distribution throughout the body. Blood transfusions are commonly required after major surgery, severe bleeding, or while treating anemia. Single RBC contributions are allowed every sixteen weeks, while apheresis-collected RBC donations are allowed every eight weeks. Donation of double the normal number of red blood cells requires a higher hemoglobin level. As they can give their red blood cells to anyone in need, donors of blood type O are in high demand. Red blood cells from these donors can be used to transfuse patients of any blood type.
The liquid portion of blood, known as PLASMA, includes essential clotting components. Plasma is used to treat patients with a lack of a coagulation factor, as seen in cases of liver failure and certain bleeding disorders. Plasma donations are accepted once every four weeks. Type AB donors are in high demand because of their usefulness as “universal” plasma donors. They can donate plasma to anyone who needs it.
Why The Need to Understand Platelets More?
Blood consists of plasma, white cells, red cells, and platelets. Platelets are responsible for maintaining a clotting blood flow. Other than that, they are the backbone of platelet transfusions. Those who need this transfusion absolutely must have it or they will die.
Many people with cancer have been saved by these platelets. This group includes people who have had an organ or bone marrow transplant. Even those who have not experienced severe trauma or are not preparing for open-heart surgery are aware of the critical need of platelets. You can find more information at the page dedicated to automatic donations.
How Long Does This Kind of Blood Donation Take Place?
Donating blood by apheresis might take up to two hours. This depends on the person’s size and proportions. Events will include things like health checks, registration for donating, and food and drink vendors. Donors can pass the time by listening to music or watching television as they wait for the operation to begin.
Who Will Be Allowed to Donate Platelets?
In order to be eligible to donate platelets for platelet apheresis, potential donors must first meet specific requirements. A good starting point would be a weight of 115 pounds. To add to that, one needs to be sixteen years old to qualify. Young people need their parents’ permission via signed consent form. At long last, a person’s health should be satisfactory.
Primarily, all of the requirements for apheresis donation must be satisfied. During the brief physical examination, platelets are counted. It’s already happening before the gift is given. Platelet donations are gratefully received. Donations from people who have taken aspirin in the last 36 hours are less likely to be accepted. The book makes a passing reference to platelet donation.
Will The Donation Be Safe For You?
Xem thêm : How To Raise Protein Levels For Plasma Donation? Step-By-Step Guide
Research shows that apheresis donation poses no health risks, thus you should look into it. If you pay, the staff will keep a close check on you. They’ll monitor you closely during the whole procedure. A small percentage of your blood’s platelets will collect in your body. Therefore, there is no risk of bleeding occurring.
In just 48 hours, your blood will have recovered its supply of platelets after their donation. We will also take care of disposing of the collection bags, needles, and tubing after each donation. Therefore, there is no way to contract the disease.
What Are The Known Side Effects?
Many apheresis donors don’t mind the pain they experience throughout the operation. The time has come to collect apheresis samples. Tinnitus is most common in the area around the nostrils and the upper lip. It was the anticoagulant used during surgery.
When this happens, alert the staff immediately. This ailment should be addressed by them. Almost certainly, a minor chill will be felt by the subject. A blanket, on the other hand, can be useful in keeping you comfortable and warm.
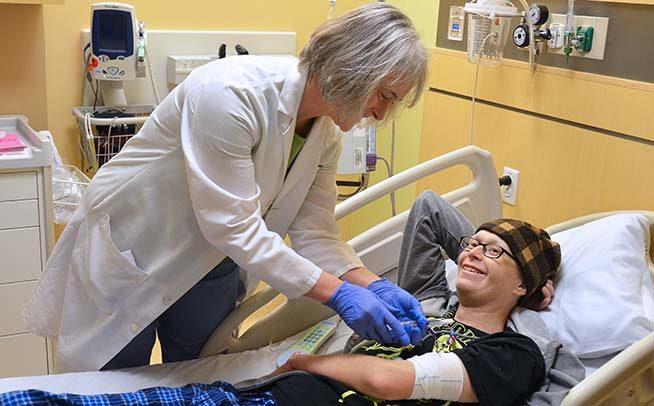
What Are The Donation Requirements?
Whenever this occurs, it is imperative that you notify the appropriate people immediately. They are the ones who should treat this illness. The subject will almost probably feel a slight shiver. However, a blanket can be a great help in this regard, since it can provide both warmth and comfort.
It is the duty of the collecting facility to keep track of annual RBC loss and blood donation totals. This means that the red blood cell count won’t rise above the safe level for whole blood donations in a given year.
Ineligible parts may be gifted by donors if they are of value to the recipient. Waiting for the OK from the attending physician is a requirement.
People who regularly give can only do it twice a week. This is doable if the collections occur two days apart. The FDA has given its blessing to a single automated plasma collecting facility, but only for a restricted amount of plasma. Each apheresis machine has its own individual settings.
Donors also need to be capable of successfully completing the multi-component collecting process. Each collected item meets the criteria for frequency of contribution and qualification. In order to determine the total plasma, the RBC losses must be determined. When it comes to medical devices, the FDA will only allow you to use them within certain safe parameters.
What Must Be Done After the Procedure?
Normal medical practice involves recording a patient’s vital statistics. The laboratory findings will also need to be assessed. This involves a complete blood count (CBC) to check for anemia and thrombocytopenia after surgery. Patients then need to be educated on the fundamentals of post-apheresis care.
Avoid strenuous activity during the first twenty-four hours and drink lots of fluids. For some patients, a wheelchair is a necessary mode of transportation. A proper notation of the gift summary is also required. This information belongs in the patient’s medical record.
Any additional problems that may occur should be noted. Everything, no matter how minor, needs to be brought to light. The temporary CVC must be flushed as well. An injection plug will be used to finish things up. When its use is no longer necessary, staff members are tasked with removing it.
What are platelets, and why are they so important?
The main components of human blood are red blood cells, white blood cells, plasma, and platelets. Blood clots can be avoided in part because of a type of cell called platelets.
Who needs platelets?
Platelet transfusions are a crucial part of several potentially lifesaving medical procedures. Patients undergoing open-heart surgery, those with cancer, those receiving organ or marrow transplants, those who have suffered traumatic injuries, and those in need of platelet transfusions all require this treatment.
How long does apheresis take?
Xem thêm : What Is The Process Of Organ Donation 6 Surprising Considerations
Apheresis donations can take anywhere from 70 minutes to two hours to complete, depending on the donor’s size and height. The procedure includes signing up, a health interview, and refreshments. It’s a terrific way to unwind to listen to music or watch movies while you save people’s lives.
Who can give platelets?
Platelet apheresis donors are held to the same standards as blood donors. To participate in this activity, you must be at least 16 years old, have a signed parental consent form, and be in excellent health.
If you fulfill the requirements, your platelet count will be checked at the mini-physical you’ll have before giving blood. If you have taken aspirin in the past 36 hours, you cannot give platelets.
Is apheresis safe for me?
Donating via apheresis does not have any inherent dangers. Each donation is carefully watched over by a group of experts to guarantee the donor’s safety. Since only a small amount of your platelets are removed, you won’t have to worry about excessive bleeding. In around 48 hours, your body will produce new platelets to replace the ones you gave away. All of the needles, tubes, and collection bags used in the process are thrown away after each donation, making it extremely unlikely that someone may contract a disease in this way.
Are there any side effects during the procedure?
Donors undergoing apheresis typically report feeling no pain at all during the collection process. Some donors report a slight tingling in their lips and nose throughout the donation process. This reaction can be attributed to the surgical anticoagulant. If the donor tells the personnel that he or she feels uncomfortable, this can be quickly resolved. While making a gift, donors may experience a tingling sensation. If you ever feel cold, you can always count on us to provide a cozy blanket.
What are the benefits of a Platelet versus a Whole Blood Donation?
- During the collection process, most apheresis donors feel no pain. Some donors report a slight tingling in their lips and nose during the process. The reaction can be attributed to the surgical anticoagulant. If the donor expresses any discomfort, the staff can take immediate action. Donors may feel a slight prickling as they hand over their money. If you need a warm blanket, you may count on us to provide one.
- Optimal apheresis collection depends on a number of factors, including donor/patient blood types, donor skills and motivation, and patient transfusion needs.
- We only give our patients the parts of the donor’s blood that they need, and we send the rest back to the donor.
The process is easy and risk-free.
Donor size and donation frequency are used to tailor blood collection processes and guarantee that only a safe amount of blood is taken.
To ensure that our donors are relaxed and pleased with their experience, we use a cutting-edge donor chair. Blood donors can relax while helping save lives by providing life-sustaining plasma, platelets, and other blood components.
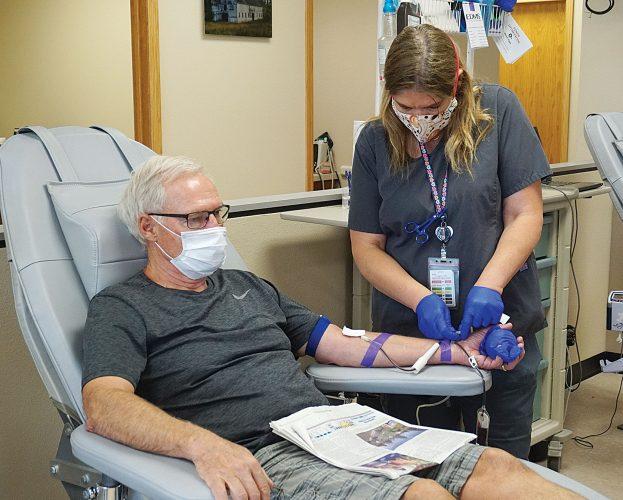
How will my blood and platelet donation help UCLA patients?
A cancer patient may require as many as two units of platelets every week.
A victim of an accident may be entitled to receive up to:
- 50 units of red blood cells
- Blood platelets from two different donors.
- It’s ten ions in plasma.
A liver transplant patient often consumes:
- Red blood cells in the amount of 25
- Twenty-five thousand red blood cells.
Stem cell transplant recipients are permitted to consume a maximum of
- There are ten red blood cells in this
- Patients receiving treatment in the outpatient setting frequently need platelet transfusions of 10 units.
A patient undergoing cardiac surgery consumes, on average:
- Seven thousand red blood cells.
- Blood platelets from two different donors.
- four units of plasma
Wrapping Up!
Donating blood by apheresis has been discussed at length up to this point. In fact, it has been shown to be effective in therapeutic settings. Systemic lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and many other conditions benefit from it as well. Donors must be in good physical condition and accord with all other requirements. It can make donating easier and safer for people who are really sick. Visit these links for more information on the topic of blood donation: what to eat before donating blood and memorial donation. We value your attention to this matter and thank you for reading.
Nguồn: https://spasifikmag.com
Danh mục: Health