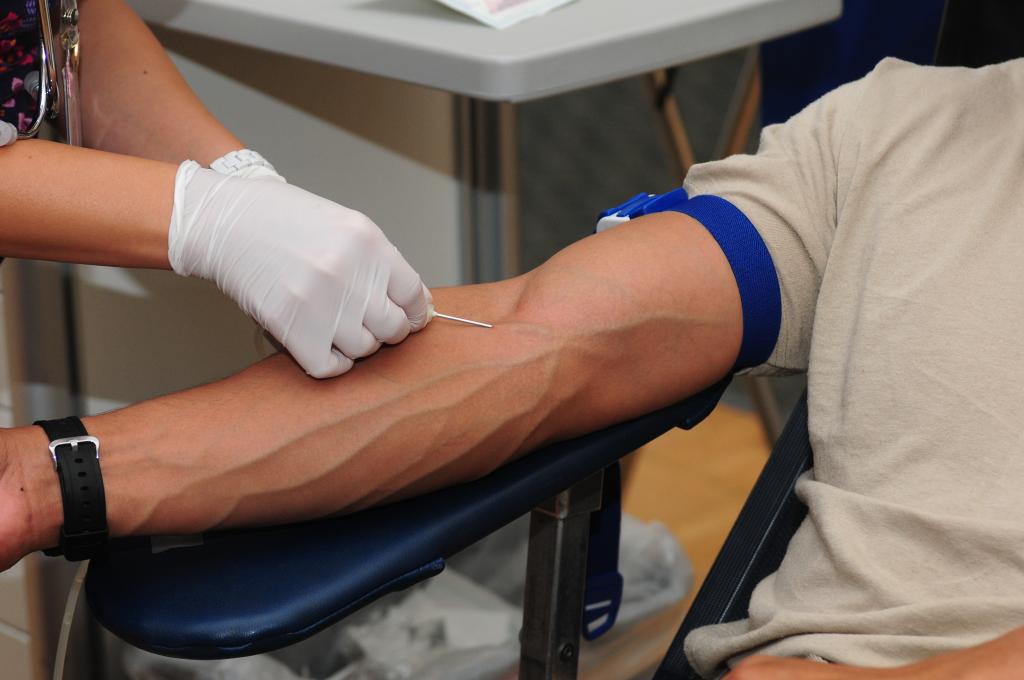
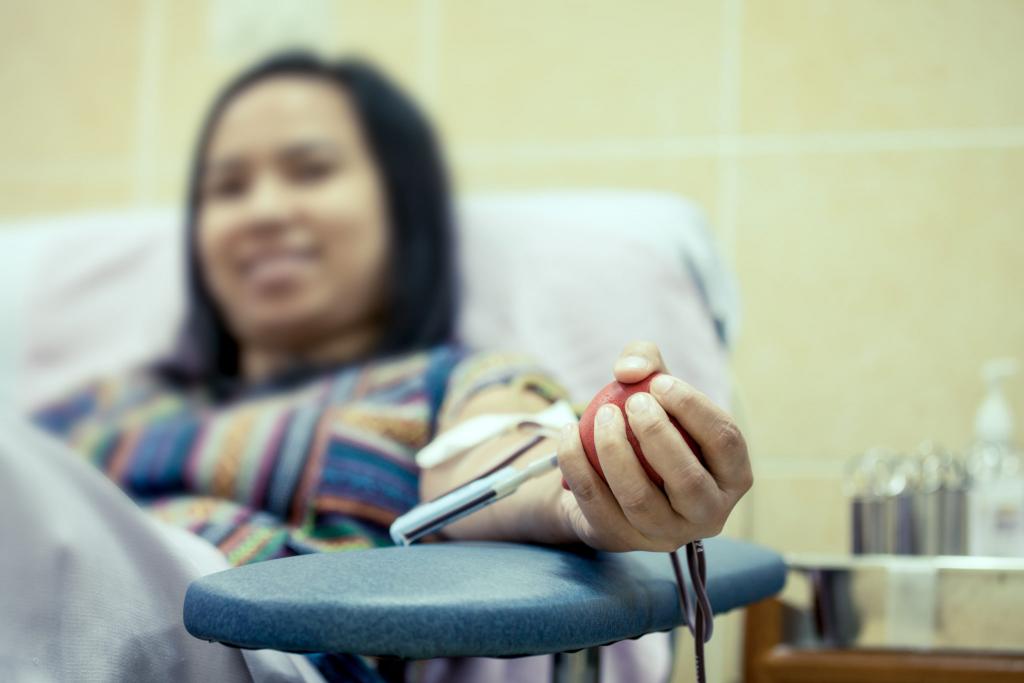
What are the potential side effects of giving blood? Your body will restore the volume of plasma you lost within a day or two. You can get along with just resting and eating healthily.
- What Is Fetal Tissue Donation? Everything You Need To Know
- How To Put A Donation Button On Your Website? 3 Easy To Follow Steps For You!
- When Need Maternity Clothes? A Comprehensive Guide
- What Is A Platelet Donation? Additional Donor Information on Apheresis Procedures
- What Is Apheresis Blood Donation? Everything You Need To Know
Only by actively seeking to replace the blood lost can it be claimed to replenish that which has been depleted. It is essential to routinely replace the blood to guarantee the proper distribution of nutrients throughout the body. The ultimate objective is to sustain a fit and healthy body.
Bạn đang xem: Are There Any Side Effects After Donating Blood? Everything You Need To Know
Avoiding tiredness after donating blood requires plenty of rest and the elimination of as many harmful habits as feasible. Overexertion from exercise has been linked to negative health effects. However, if complications after donating blood can be avoided, the body’s recovery time may be reduced.
What Is Blood?
The blood is the primary means through which nutrients have been distributed throughout the body. Blood carries hormones and antibodies around the body and helps the immune system fight off infections. If a person’s blood has enough nutrition, their immune system is better able to fight off illness.
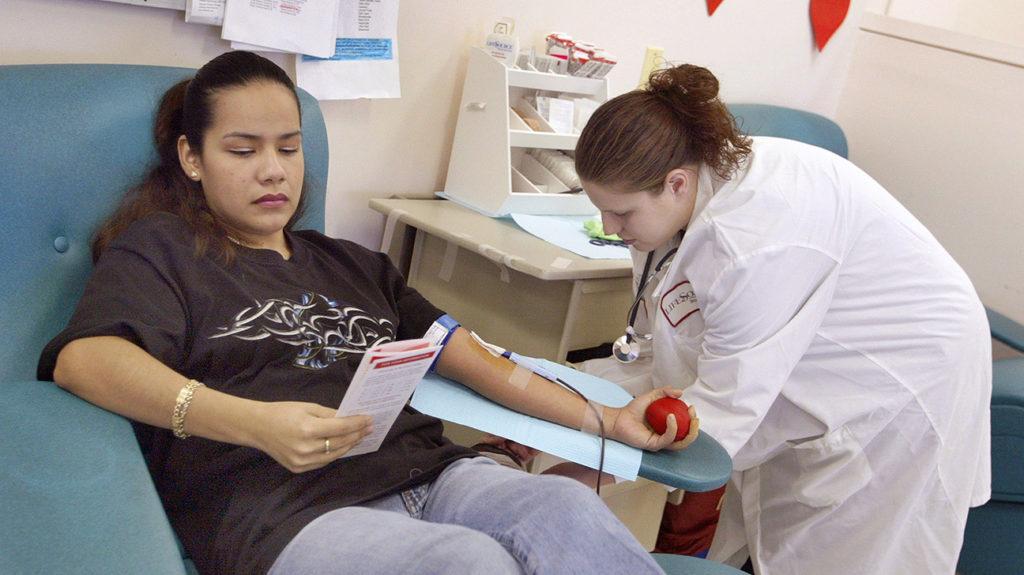
The function of the arteries is to transport nutrients, oxygen, and waste products to and from the body’s organs and tissues. When seen in movement, blood takes on a more viscous appearance. It’s crimson, thick, and compact when you try to touch it.
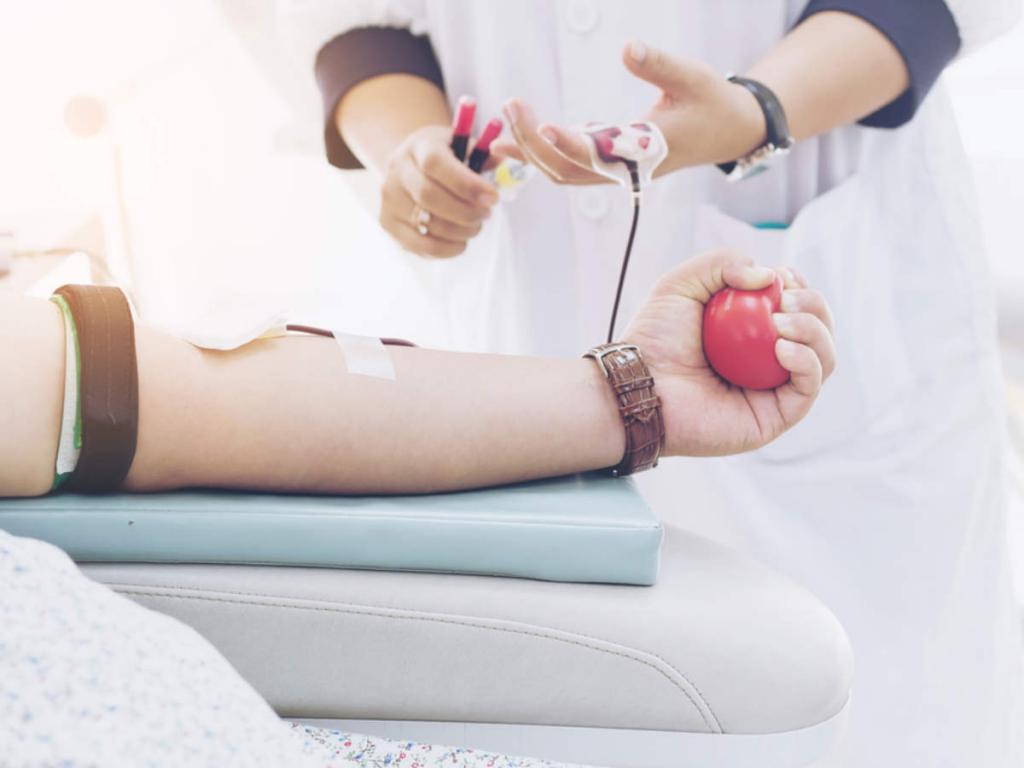
What Is A Blood Donation?
When time is of the essence, a person may decide to donate blood whether or not they want to. Donated blood can be used for both transfusions and therapeutic purposes. Donating blood helps ensure that the blood supply will continue to replenish and remain healthy for future generations. Blood donation is a selfless act that benefits not only those in need but also the donor. Your blood fat levels are being regulated. Preventing arterial plaque buildup and lowering cardiovascular disease risk is extremely important. Recognize the significance of giving two units of red blood cells.
Are There Side Effects After Donating Blood?
Many different physiological responses might occur after donating blood. You will be informed of these risks after giving blood.
#1. Dizziness
After giving blood, you could feel a little lightheaded. The reduction in blood pressure after donating causes this. Donors who feel dizzy after giving blood should take it easy for a while.
#2. Easily to became tired
Those who have donated blood may feel tired for a while afterward and should rest until they feel better. It’s possible that rehydrating with water will make you feel better physically and mentally. When you give blood, your body needs rest. A nap and a night’s sleep will help it recover.
#3. Minor swelling
Some people experience mild edema after giving blood. The place where the needle was inserted may enlarge. Ensuring adequate sleep and avoiding severe physical exertion can aid in recovery.
Why Do We Donate Blood?
In rare cases, blood donors may experience mild edema. In the place where the needle was inserted, swelling is to be expected. A good night’s sleep and a reduction in strenuous activity will speed up the healing process.
What are the benefits of donating blood?
The availability of blood for patients in need is guaranteed thanks to generous blood donors.
Donating blood could improve the emotional and physical health of the donor as well as the beneficiary.
Saving lives
The American Red Cross reports that every two seconds, someone in the United States requires blood, and that a single blood donation can save the lives of three people.
Emotional and mental health
Those who volunteer often report feeling better afterward.
According to the UK-based Mental Health Foundation, helping others can result in the following:
- increased joy in one’s life
- Decreased Anxiety
- tighter bonds with neighbors
- a life with fewer moments of solitude
- Negative emotions were dampened or eliminated.
Physical health
Donating blood also entitles the donor to a free physical. Before donating blood, potential donors will be interviewed by staff members at the center.
Ability to perform a certain task will be measured via a test.
- frequency of one’s heartbeat
- concentrations of hemoglobin.
- temperature
- pulse
When people get these checks done, they may find out about hidden health problems they’ve been ignoring.
Xem thêm : How Does Egg Donation Work? Things To Consider
There is some evidence that donating blood is beneficial for cardiovascular health.
Researchers found that the cholesterol levels of 82 healthy male and female blood donors dropped significantly between 2012 and 2013.
Regular blood donors had higher cholesterol levels than nondonors, but lower levels of indicators signifying an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. Researchers said they need to see these results confirmed in a larger study.
In 2019, researchers conducted a massive study to determine how regularly donating blood affected the health of 159,934 people.
Regular female blood donors may have a lower risk of cardiovascular disease than men, according to new research.
Donors who gave blood more often than others had a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease.
Physical side effects
Donating blood might cause temporary bodily reactions in certain people.
Bruising and pain
Some people may experience short-lived physical effects after donating blood.
A non-profit company, Bloodworks Northwest, says that using a compress can assist reduce swelling and pain.
A compress can help alleviate swelling and pain, according to Bloodworks Northwest, a non-profit organization.
If you’re experiencing any pain, applying a cold compress may assist. In cases of severe or ongoing discomfort, it is recommended that patients see a doctor.
Minor bleeding
Donating blood might cause mild bleeding at the injection site in some patients. It is possible to prevent this by leaving the bandage on for at least four hours after a donation.
If the wound continues to bleed after 4 hours, they can apply pressure for 2-5 minutes and leave the bandage in place.
Fatigue and lightheadedness
Tiredness, dizziness, lightheadedness, and nausea are all possible side effects of blood donation. Reduced blood pressure for a limited time
If you’re feeling lightheaded, try sitting with your head tucked in between your knees. When lying down, keep your legs elevated to reduce the risk of rolling over. If symptoms persist, people should see a doctor.
Donors should replenish their fluid stores by drinking plenty of water before and after giving blood.
Before giving blood, the American Red Cross advises volunteers to drink 16 ounces of water and 8 ounces of fluids afterwards.
Donors should not consume any alcohol in the 24 hours before up to or following their donation.
You can replenish your body’s fluids during the next three days by drinking plenty of water.
It is possible to rebuild iron stores by consuming a healthy diet rich in iron-rich food.
- Consuming a balanced diet that’s high in iron-rich foods will help restore depleted iron stores.
- turkey
- spinach
- shrimp
- Specifically, we’ll be discussing sweet potatoes.
- broccoli
- tofu
- beans
- dishes made from wheat flour
Combining iron-rich meals with vitamin C helps with iron absorption. Vitamin C-rich foods include:
- tomatoes
- Citrus fruits, such as oranges and lemons, are examples.
- Peppers of various hues
Xem thêm : How To Make A Donation Box Out Of Cardboard? Step-By-Step Guide
Regular use of an iron-fortified multivitamin may also help replenish iron stores in regular donors.
Donors should take it easy for the next 12 hours after giving blood and avoid doing any strenuous activity. Naps are helpful because they allow the body to adjust to the blood loss.
Blood donors are welcome to take advantage of the center’s waiting area after their donation is complete. This means that they can seek prompt medical attention in the event that they experience any unfavorable reactions.
After the lecture, attendees may be treated to a little snack and drink. After a rest, there will be no lingering affects, so people can go home.
Donors should consult their doctor if they have any serious or persistent symptoms after giving blood.
Advantages of donating blood
There are a lot of positives associated with blood donation. It has the potential to reveal latent health problems, reduce the likelihood of cancer and cardiovascular disease, and aid in the maintenance of health over the course of a person’s life. Most crucial, keep up a healthy way of living. Giving blood benefits not only the person who receives it, but also the donor and the organization that receives it. While donating blood can be intimidating, it’s a rewarding experience that helps others in need while also replenishing your own blood supply. Donating blood on a regular basis has many health benefits.
Summary
Giving blood benefits those who receive it, but it also has many positive effects for the donor and their loved ones.
It’s possible that blood donation could cause dizziness, minor bruising, or little bleeding in certain people. Restoring lost fluids and iron stores can be aided by eating meals high in both.
Avoid strenuous activity for a while after giving blood, and keep the bandage on the injection site for a while to help the body heal faster.
When symptoms are severe, one should get medical help or dial 911.

FAQs
How much blood should you donate?
One unit of blood, or about 350 milliliters, is normally drawn from a healthy donor when a full blood count is conducted. Every three months, a healthy adult can donate 350 ml of blood without risk.
Is it healthy to give blood?
Donating blood to those in need is a noble act. The human body can replenish donated blood in 4 to 8 weeks, whereas blood plasma can be replaced in 48 hours. Donating blood is a great way to reduce your risk of cardiovascular disease by eliminating excess iron from your system. Self-renewing blood is beneficial for both the pancreas and the liver.
Does giving blood lower your immune system?
There may be a temporary drop in several types of immune cells, like circulating serum protein and antibodies, after blood donation. In the event that your body requires these antibodies, however, you can anticipate a return to normal blood levels in a few of weeks.
Does donating blood clean your system?
Donating blood aids in the elimination of toxic iron from the body, which can be a cause of the disease known as hemochromatosis. Donating blood on a regular basis can help keep iron levels in check and lower the danger of a heart attack. Improved health and performance can be shown 48 hours after donating blood as the body works to replace the blood volume lost during the process. According to the Mental Health Foundation, giving blood has positive effects on mental health since it helps relieve stress, boosts emotional well-being, lessens negative thoughts, and infuses a sense of connection via helping others in need.
Do blood donors live longer?
Donating blood can increase a person’s lifespan since regular checkups reveal any health issues early and can reduce the likelihood of deadly diseases like cancer and heart disease. Your pancreas and liver will function better, which will lengthen your life.
Why should you not donate blood?
If your hemoglobin or blood pressure is low, you shouldn’t give blood. If you have a fever, persistent sore throat, or cough, you shouldn’t give blood. The recipient of the blood could develop the disease as a result. If you have recently taken antibiotics, please wait at least two weeks before donating blood. Avoid giving blood if you’re underweight because it could make you sick or lead you to pass out. To avoid hepatitis infection, don’t give blood to those who have had body piercings or tattoos done.
Can I give blood if I smoke?
Anyone with a low hemoglobin level or low blood pressure should not donate blood. If you have a fever, persistent cough, or other infectious disease, you shouldn’t give blood. By receiving infected blood, the donor risks contracting the disease. If you have recently been given antibiotics, please wait to donate blood. If you are underweight, you shouldn’t donate blood since you might feel sick or pass out. Don’t give blood to those who have had tattoos or piercings done to reduce the risk of hepatitis infection.
How often can I donate blood?
Donating blood is safe every 56 days because the body can replenish its supply in just four to eight weeks. You are allowed to donate plasma up to 13 times per year, and platelets up to 24 times per year (one per week). There is a minimum interval of 112 days between RBCS donations.
Donating blood is a great way to help others and have a positive impact on the world, but it also has practical benefits like facilitating frequent illness screenings, which can help you live a longer, healthier life. If you get sick, you can rest assured that you’ll have access to top-notch care that won’t put a strain on your wallet.
Conclusion
What are the potential side effects of giving blood? In my opinion, the response must be yes. Therefore, this essay can help you become a better donor by raising your awareness of your body. Donating blood saves lives and brings comfort to those in need.
Nguồn: https://spasifikmag.com
Danh mục: Health