The most popular air conditioner is the 12000 BTU model, but there are many more. This is a frequent inquiry, especially when only one AC unit is being purchased. A typical household uses about 900 watts per hour when running a 12000 BTU air conditioner. A home’s heating and cooling system is one of the most utilized systems in the home.
- How To Unclog Air Conditioner Drain? Easy Step-by-step Guide
- How Often Do You Have To Drain A Portable Air Conditioner? A Must Read Guide
- How to Recline Britax B Agile Stroller? Step by Step Instructions
- What Is A Coil On An Air Conditioner? How Does it Work?
- How To Clean Faux Leather Exterior? A Few Tips to Remember
However, if you live somewhere with a constant, freezing temperature, your air conditioner can stay in the closet. The British Thermal Unit (BTU) is an important metric to examine as it relates to air conditioning. Use the British Thermal Unit to estimate how much power your air conditioner will need (BTU). Keep reading, my friends, because there’s more information underneath!
Bạn đang xem: How Much Electricity Does A 12000 BTU Air Conditioner Use? Perfect Information For You!
The Amount Of Electricity A 12000 BTU Air Conditioner Use
To cool a room that requires 12000 BTUs, how much power would you need? Many people use air conditioners to cool down on hot and muggy days. Therefore, the high cost of maintaining these gadgets is unexpected. Consider the British Thermal Unit (BTU) when considering the power consumption of air conditioners.
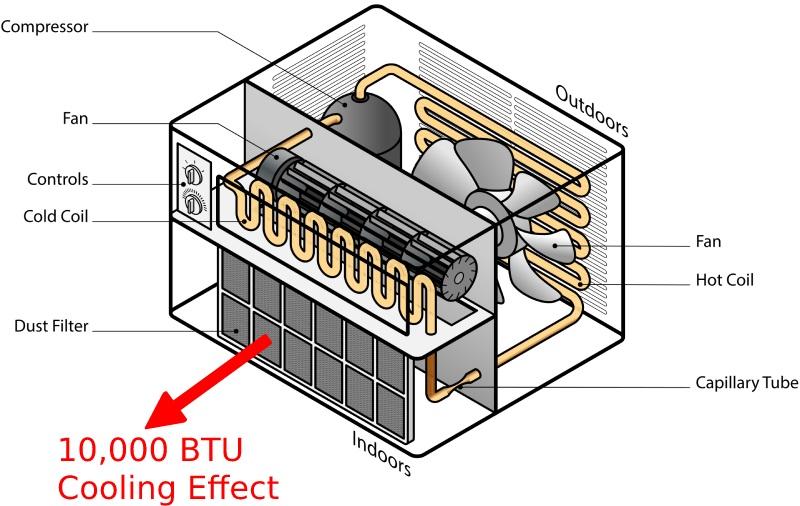
The BTU output of an air conditioner is directly proportional to the amount of electricity it consumes. An air conditioner with a capacity of 12,000 BTUs consumes about 900 watts of electricity each hour.
So, we’re moving toward a SEER minimum of 13. Not all appliances with 12000 BTUs can make that claim. In all other circumstances, it would depend on the make and model in question. Your bill could go up, and we’ll discuss the options with you if that happens.
How much would a 12000 BTU air conditioner add up to the bill?
Using an air conditioner will significantly increase your monthly electricity bill, but not all units are created equal. This 12000 BTU air conditioner has a yearly cost of about $400. This will allow them to maintain a cozy temperature within their homes. It’ll set you back a little more than a year’s salary. We still didn’t know how much it would cost each month.
Air conditioners don’t have any mysterious fees attached to them. A central air conditioner with a BTU rating of 12,000 is suitable for cooling a medium-sized room or building. However, we must remember that it uses about 900 watts per hour of electricity, making it both expensive to purchase and maintain.
How much is 12 000 BTU when used daily?
To cool your home for just 8 hours a day at a cost of $34.10 a month, you’ll need an air conditioner with a 12,000 BTU capacity. Thankfully, cooling off won’t require constant attention from the AC. Only if it’s really hot outside and humid where you are. An air conditioner with a BTU rating of 12,000 can be run on a total of 240 watts of electricity. You may calculate your monthly electricity costs using the converter.
Where To Buy 12000 BTU Air Conditioner?
Due of its usefulness and potential cost savings, it could be a good investment. Don’t worry, we’ll help you narrow down your options for a 12000 BTU air conditioner. Two alternatives are provided for your consideration. Take a look at these.
Option #1. Go to the appliance center
It can be a good idea to get it because of how effectively it performs and how much money it can save you. You may rest easy knowing that we will provide you with options for locating a 12000 BTU air conditioner. Choose from two convenient alternatives. Check these out as an illustration of the aforementioned paraphrase.
The only way to safely shop at malls is to live in a region that has not been severely affected by the virus. However, it is prudent to exercise cautious if the pandemic has reached your area.
However, this is the safest and most reliable way to acquire an air conditioner. You can ask anyone working there, including the manager, for help or more information. The warranty and the way it is presented are both top-notch.
Option #2. Buy one online
Cooling systems that have a BTU rating of 12000 can be hard to come by. However, this is why some people choose making a purchase for one online. A/C units can be purchased from a number of different brands and can range in price and name recognition.
Making a decision is preferable to accepting the default option. Select the more pricey but better quality option if at all possible.
For those on a tighter budget, however, we suggest going with a far more reasonably priced option that will still serve you well for many years. Don’t take a chance on a cheap item that can tempt you into making additional purchases. Consider it instead as an investment in the future.
How Much Power Does An Air Conditioner Use? Rough Numbers
There are a number of variables that might impact how efficiently your air conditioner uses energy. Due to this, the numbers provided to you for your home may vary from those you find online. Those details will be covered in the next section, but first, let’s take a look at some aggregate statistics. As you may imagine, these will change depending on the specific model of AC unit you have.
How Much Power Does A Central Air Conditioner Use?
In hot weather, a typical central air conditioner uses between 3000 and 3500 watts per hour of electricity. This is the ideal temperature for air conditioners to be set in Phoenix and other hot climates for the bulk of the year. The “fan alone” setting on a central air conditioner can reduce its power consumption to as little as 750 watts per hour.
How Much Electricity Does A Portable Air Conditioner Use?
Mid-sized portable air conditioners consume around 2900 watts per hour. However, huge central air conditioners consume about 4100 watts per hour. This essay will educate you on the different air conditioner sizes and how they are measured.
Window Air Conditioner Energy Usage
This size of window air conditioner has an average power usage of roughly 930 milliwatts per hour. Smaller machines typically need 500 watts per hour, whereas larger ones use 1440 watts per hour.
Making Cents Of This Data
Your major concern with energy usage is usually not the nominal wattage figures unless you’re trying to cut carbon emissions. It’s more likely that you’re worried about your financial situation. Arizona’s high electricity rates of 12.8 cents per kilowatt-hour can be attributed to the state’s warm climate and subpar air quality. When you have this data on hand, figuring out how much energy will cost is a breeze. For actual costs, multiply the number of hours your air conditioner is on by 12.8 cents per hour and divide by your estimated wattage usage per hour.
It’s crucial since air conditioners can’t run for extended periods of time nonstop. Instead, they are only turned on and off when absolutely essential. Most air conditioners run for 15 minute cycles as infrequently as twice an hour, so when you turn it on, you’ll notice an abnormally high usage per hour amount. All things considered, Arizonans spend around $400 year on their air conditioning costs.
Be aware that these figures are tailored to the state of Arizona and are based on the average energy consumption and cost of electricity for air conditioners in that state…. These numbers could be slightly vary depending on your region. Federal statistics show that those in the warmer states of Arizona, Nevada, and New Mexico spend approximately twice as much as those in the colder regions.
Factors That Affect Air Conditioner Electricity Usage
Having answered the question of about how much power an air conditioner uses per year, we can now examine the specifics that can change those numbers.
Your Air Conditioner’s Capacity
Energy consumption is mostly determined by the capacity of the cooling system. British thermal units are used for the measurement of heat (BTUs). Approximately 20 British thermal units (BTUs) per square foot of living space is typical, though this can vary greatly depending on climate and design considerations. More cooling capacity and therefore more energy will be required the larger the area being cooled.
Your Air Conditioner’s Efficiency Rating
All air conditioners won’t be created equal, even if they have the necessary BTUs. AC units are rated according to their Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER). It’s the cooling capacity expressed as a fraction of the seasonal electricity consumption per hour. The greater the SEER number, the more efficient your air conditioner is. There are units available with ratings as high as 25, but 13 or 14 is the federally mandated minimum for your location.
Climate
The average New Yorker can get by with less powerful cooling equipment than someone living in Arizona. Greater energy consumption is inevitable with the addition of those BTUs. It’s also a smart idea to invest in a pressure reducing valve (PRV) to make sure your plumbing fixtures never leak.
Your Maintenance Routine
If you’re moving from New York to a place like Arizona, you’ll need a more robust air conditioner. Using more BTUs will increase energy usage. To ensure that your plumbing system is operating as it should, it is recommended that you install a pressure reducing valve (PRV).
Temperature Settings
Keeping the temperature at the same level throughout the day is a simple technique to increase the effectiveness of air conditioners. In many cases, the manufacturer suggests keeping the temperature at 75 degrees all the time. Changing the temperature on your air conditioner during the day or turning it down to a lower setting will increase your energy bill.
Insulation
The efficiency of your air conditioner can be maximized simply by keeping the temperature constant throughout the day. Manufacturers’ suggested settings often center around 75 degrees. Energy consumption can be raised if the air conditioner’s temperature is lowered or adjusted during the day.
How Much Power Does My Air Conditioner Use? Conclusion
Although air conditioners consume a large amount of energy, the precise amount is affected by many variables. One hour of operation from a central air conditioner is possible at a rate of 3000–3500 watts per hour. Compared to the 2900-4100 watts used by portable air conditioners, window units only use 900-1440 watts.
Make sure you get the most out of your air conditioner by consulting a local expert before making a purchase. Call American Home Water and Air, fill out our contact form, or go through our Frequently Asked Questions to find out more about what we can do for you. Sun City, Glendale, Mesa, Scottsdale, and the greater Phoenix area are all within our service area.
How Does One Determine The Efficiency Of An Air Conditioner?
It is helpful that air conditioners for rooms can be sorted by their energy efficiency ratio (EER). The EER, or Energy Efficient Ratio, measures how well a product uses energy. By comparing the cooling capacity to the watts, the EER calculates the efficiency of an air conditioner. To put it another way, the power consumption of a 24,000 BTU [PDF] unit with an EER of 10 is 2,400 watts (24000/2400).
Due to their high power consumption, air conditioners should have an EER of at least 11. The good news is that you can readily locate these.
The rating for an air conditioner with 18,000 BTUs.
Your electricity costs are only related to the ‘STD INPUT POWER’ rating on this label. The power output of the gadget is indicated here in watts.
The maximum input consumption is the power required during starting and does not exceed the locked rotor current at any time during operation. Do not worry about the impact on your electricity bill, as it will not require more than a few milliamps for more than a few seconds.
Capacity Btu/h refers to the cooling capacity of an air conditioner in British Thermal Units per hour. It claims 18,000 BTUs of output capacity. We were able to determine that this device has an EER of 9.47 by dividing the BTU/h rating (18,000) by the usual power input rating (100). (1900). A more efficient approach is possible. Keep in mind that a greater EER is preferable.
Keep in mind that the “REFRIG”-labeled R410A refrigerant is a more environmentally friendly option than the “R22” refrigerant. R410A is widely available because it is used in virtually all modern residential air conditioners. R22 units are becoming more expensive to maintain as R22 refrigerant is being phased out or becoming increasingly scarce.
Are Air Conditioners Expensive To Operate?
Air conditioners are expensive to run since they consume a lot of energy. If you only need to chill one room, the cost of running the air conditioner will be much lower than if you need to cool three or more rooms at once. More rooms typically mean a larger HVAC expense, so this is another crucial factor to think about.

The type of home electronics you have an effect on how much energy your air conditioner uses. If you simply have one light bulb per room and no recessed lighting, you can expect to cut your lighting use.
On the other hand, if you use several high-wattage incandescent bulbs in each room, you may soon rack up a hefty power bill. The total cost of owning an air conditioner is based on its cumulative power usage.
Only cool the room in which you want to spend the most of your time during the day to save energy consumption (that could be your home office or bedroom, for example). You should be alright as long as you don’t spend too much time in the other rooms.
Effect Of Unit Size On Air Conditioner Power Consumption
The energy efficiency ratio (EER) may be slightly lower than typical units due to the unit’s smaller size. Given your routine, it’s possible that you’ll have to spend more money on a smaller air conditioner than you had planned.
Using a small unit in a room bigger than its suggested size can result in a long cool-down time, making you reluctant to turn off the unit (this is a terrible waste of energy). Some folks may opt to purchase slightly larger air conditioners to avoid having to wait.
Thus, you may be hesitant to turn off tiny units when used in rooms larger than the optimum size since you don’t want to wait for them to cool down again (this is a terrible waste of energy). Some people, in order to avoid having to wait, may decide to acquire air conditioners that are slightly larger than their needs.
Power Consumption Of Air Conditioners – Ordered By Unit Size
Power Consumption Of 5,000 BTU Air Conditioners (0.41 Tons/1.4 kW)
Xem thêm : How To Fix An Air Conditioner Fan Motor? Easy Step-by-step Guide
Since you might not want to wait for the little unit to cool down again, it might be difficult to turn it off when it is being used in a space that is far larger than its recommended capacity (this is a terrible waste of energy). For the sake of not having to wait around, some people opt for slightly larger air conditioners.
For cooling purposes, a 5,000 BTU air conditioner will typically consume between 446 and 580 watts of power (most of the units assessed for this average were window units, as 5,000 BTU split units are uncommon).
Air conditioners with a BTU rating of 5,000 are frequently found in college dorms and other small dwellings. The most prevalent type is those that are installed in windows. DIY installation of window air conditioners is common because you don’t have to drill holes in your landlord’s walls.
Estimated Monthly Energy Usage:
51 to 59 kWh.
The average electricity rate in the United States is $0.12.
Costing between $6.22 and $2.08 every month over the course of a year.
Ambient temperatures are expected to be at least 25 degrees Celsius. The inverter-type of AC unit is not covered here.
Find and shop for the least power-hungry 5,000 BTU air conditioners with the help of our AC comparison tool.
Power Consumption Of 9,000 BTU Air Conditioners (0.75 Tons/2.6 kW)
Power consumption for 9,000 BTU air conditioners ranges from 800 to 900 watts (the higher the wattage, the less efficient the machine is). There is a sweet spot between 350 and 400 square feet for a 9,000 BTU air conditioner (this average applies to both window and split units).
It is recommended to consult an expert before making any purchases, however a 10,000 or 12,000 BTU air conditioner may be sufficient for a 350-400 square foot area.
Purchasing an overly large air conditioning unit might negatively affect its efficiency and could even encourage the growth of mold due to the high levels of humidity it creates.
If you obtain an inverter type, their electricity costs will be comparable to those of smaller units because they don’t have to operate as long. Standard air conditioners with 24,000 BTUs use somewhat more energy than average since they provide less cooling per watt of power used.
Estimated Monthly Energy Usage:
Energy usage is about in the range of 71 to 95 kWh.
The average electricity rate in the United States is $0.12.
Monthly costs between $8.52 and $11.40
Ambient temperatures are expected to be at least 25 degrees Celsius. This class encompasses both inverter and non-inverter devices.
Our air conditioner finder can help you zero in on the most power-efficient models among those that produce 9,000 BTUs, and we sell them, too.
Power Consumption Of 18,000 BTU Air Conditioners (1.5 Tons/5.2 kW)
There are a few odd air conditioner sizes in the 12,000-18,000 BTU range, such as 13,000 BTU, 14,000 BTU, and 15,000 BTU, and room size calculations may yield results that do not match any unit (or exceedingly rare units) on the market (or even rarer) (such as 16,000 BTU).
In other words, if your installation couldn’t find an air conditioner with a higher BTU rating than 18,000, you should expect to be offered a unit that is considerably (or significantly) larger.
In general, 1.5-ton air conditioners have EER ratings between 11 and just over 12, with power consumption ranging from 1,470 to 1,614 watts.
It is important to remember that the wattage does not represent the overall power consumption of the units, even when set to the minimum allowable temperature and the maximum allowable fan speed. The EER is typically printed on the energy label, which is yellow in color.
There is no such thing as second best. Air conditioners with an EER of greater than 12 are the way to go if you can afford it. The gap between versions 11 and 12 is not huge, so you might want to invest in a gadget with solid support (this entails buying it from a reputable store that offers free repairs within a reasonable warranty period).
Inverter air conditioners are available in this price range as a result, and inverter systems can save as much as 50-60% in energy costs compared to non-inverter equivalents under certain conditions.
If you’re also curious about how much energy different sizes and types of refrigerators use, Kompulsa provides a page with that information.
Monthly Estimated Energy Use:
At a power level between 170 and 185 kilowatts
The average electricity rate in the United States is $0.12.
Approximately $20.28 – $22.20 each month
Ambient temperatures are expected to be at least 25 degrees Celsius. This class encompasses both inverter and non-inverter devices.
Power Consumption Of 24,000 BTU Air Conditioners (2 Tons/7 kW)
New 24,000 BTU air conditioners have an Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER) of 8.5 to 12.5, making them less efficient than smaller models (this applies to both split and window units).
There is a 500 kilowatt-hour (kWh) to 2,823 kilowatt-hour (kWh) power range. Despite their low efficiency, these units are among the most widely used (possibly because they cool rooms very quickly, as well as the popularity of the open floor plans).
You can compare the average power consumption of your air conditioner to that of contemporary units and the values provided below with the help of a ‘Kill A Watt’ or equivalent energy meter.
This means they can still be considered an option (not that you have much of a choice, as some rooms require units of this size). Since it could take a while for them to cool down, they might not want to turn them off.
So, a 24,000 BTU air conditioner’s energy utilization could be lower than that of a 12,000 BTU air conditioner (assuming it is used in the same room).
A 24,000 BTU air conditioner is not required but does use an average of 228 kWh/month of electricity in the United States, as reported by the Department of Energy. These modules can be compacted to meet space constraints.
This works out to about $27 USD per month as a payment. In some cases, an inverter air conditioner can reduce energy consumption by up to 60%.
Electrical Ratings
Amperage
This works out to about $27 USD per month as a payment. In some cases, an inverter air conditioner can reduce energy consumption by up to 60%.
This amounts to roughly $27 USD per month in repayments. The use of an inverter in an air conditioner can sometimes cut energy use in half.
Power Consumption Of 28,000 BTU Air Conditioners (2.3 Tons/8.2 kW)
Effectively cooling a room of up to 1,900 square feet requires a unit with 28,000 BTUs or more (although keep in mind that this does not include rooms in megathermal/tropical regions).
The power of most 28,000 BTU heaters is between 2,800 and 3,100 watts, which is in the 9-10 EER range. These units don’t have the best EER ratings, but larger ones, like the 24,000 BTU, typically have lower EER rates than smaller ones.
The power of most 28,000 BTU heaters is between 2,800 and 3,100 watts, which is in the 9-10 EER range. These units don’t have the best EER ratings, but larger ones, like the 24,000 BTU, typically have lower EER rates than smaller ones.
Most 28,000 BTU heaters have an output of 2,800 to 3,100 watts, putting them in the energy efficiency range of 9 to 10 EER. The efficiency ratio (EER) of these units isn’t great, but larger models, like the 24,000 BTU unit, typically have lower EER ratings than smaller models.
Estimated Monthly Energy Usage:
Power consumption of 330-357 kWh
The average electricity rate in the United States is $0.12.
Spend between $39,60 and $42,84 every month.
Ambient temperatures are expected to be at least 25 degrees Celsius. This class encompasses both inverter and non-inverter devices.
Reducing Air Conditioner Energy Usage/Cooling On A Budget
If the previous information has you worried about the energy consumption of air conditioners, relax. The following advice can assist you in greatly decreasing your use of (which are intended specifically for residential air conditioners, although they may be helpful in other cases).
Maintenance
Xem thêm : What Causes Condensation On Air Conditioner Vents? Helpful Guide
Air conditioners rely on the movement of air via a plethora of minute openings. Check to see that the fins, filters, and coils of both the condenser and evaporator are clean. Having any of the following dirty parts can reduce airflow.
Clogged condensers can cause overheating, poor performance, and even compressor failure. If the evaporator in your air conditioner freezes, it will no longer cool the air and will be completely worthless. Less energy is required to run an air conditioner when its evaporator is not clogged.
Equal filters are used. Hire a professional to clean the condenser and evaporator, as these components are not accessible to the average person.
Inverter Air Conditioners Vs Standard Units
A variable speed air conditioner is the quietest option available (VSA). In order to keep the house at a constant temperature, you can set the thermostat to turn on and off at predetermined intervals.
In contrast, inverter units adjust the speed of their compressors using technologies like pulse width modulation (PWM) and variable frequency drives.
Some inverter air conditioners utilize the same PWM motor control technology. Since they don’t have to run at full speed all the time, PWM allows them to function at reduced speeds (which means lower power consumption and lower noise levels) when cooling need is limited.
If you have an inverter unit, you can quickly drop the room temperature by having the heater turn down to a lower level when the power is shut off (but it will take a moment for the room temperature to change).

When An Inverter Air Conditioner Is Not Worth It
Buying an inverter air conditioner is a good idea if you use or need it frequently, but it’s not worth the extra cost if you rarely use it.
Getting a cheap air conditioner is a good idea.
You put in a lot of hours at the office.
Your dwelling is a flying machine. Some people only visit their hometowns once every few weeks or months due to their constant travel.
When An Inverter Air Conditioner Is Worth It
Adjusting the temperature with an inverter air conditioner is much simpler than with a conventional unit. If you use your air conditioner frequently for extended periods of time, an inverter model will pay for itself quickly.
Several manufacturers claim that inverter air conditioners can cut energy consumption by as much as 70 percent compared to non-inverter models. The savings are significant if you reside in an area where power costs more than $0.20/kWh, but they are negligible if electricity costs less than $0.10/kWh where you currently live.
In these cases, inverter air conditioners are the best option because they typically pay for themselves within a reasonable time frame.
Daily home time exceeds eight hours.
You’re used to putting in long hours, so it’s not unusual for you to do so. Assuming you sleep during the day, this covers any shift that takes place at night.
Buy White Curtains
White curtains are effective at reflecting solar heat back into the atmosphere. Direct exposure to sunshine, which becomes heat once it enters your room, may make the situation worse.
Insulate Your House – The Most Effective Option
The quantity of energy required to cool a building can be drastically reduced with good insulation. However, installing insulation in your home can help you save money on your heating bills by reducing heat loss to the outside. Insulation blocks heat transfer into and out of a structure.
The R-value of insulation, which indicates how well it insulates, should not be overlooked. Your monthly energy costs are proportional to the R-value of your home’s insulation.
Use A Fan
Arrange a freestanding fan in front of your face. Raising the thermostat on your air conditioner may help you cool off because of the evaporative cooling effect of fans. Turn it on only if you plan to raise the thermostat setting to offset the additional power consumption of the fan.
Standing fans with a diameter of 20 inches or less are preferable for areas with many people since they generate less noise and consume less power. If you don’t point the fan at yourself, it won’t cool you off. If you don’t like the fan blowing straight down on you, try setting the oscillation to the whirling position. The recommended fans typically have a power consumption between 50 and 100 watts.
Desk fans well under 16 inches (you’ll most commonly encounter 8 inch ones) may be sufficient if used on the desk (directly next you) as designed, or if your room is only slightly too warm. I like these because I can just pick them up and carry them from one place to another.
Awnings
If you place it on your desk (next to you) as intended or if your room is only somewhat hot, a desk fan under 16 inches (most usually seen at 8 inches) in diameter may be sufficient. I like these because I can just pick them up and carry them from one place to another.
Point The A/C Vent At Yourself, And Turn Up The Thermostat Temperature
This endeavor was a smashing success in my book. If you can, direct the air conditioner’s vent toward yourself to take advantage of the evaporative cooling effect. This will allow the air conditioner to focus more on cooling you than the furniture in the room.
Perhaps this is one of the riskier options available. Make sure the device is always clean for your own protection.
Set The Thermostat Temperature Wisely
If you have a thermostat, set it as high as you can stand to keep it. Keeping the temperature just right means keeping the unit on for longer. By setting the thermostat lower, you increase the amount of energy an inverter appliance uses by making the compressor pump refrigerant at a higher rate. A 16-degree drop in temperature from a thermostat set at 80 degrees Fahrenheit will result in a savings of 8 percent on cooling costs.
Cool Only The Areas You Need To
Having a unit in each room or a central air conditioning system may seem like a good idea to “keep the house cool,” as some may put it. Don’t chill down the entire house with the air conditioner if you’re only going to be in the room for a few minutes.
The 7 Best Energy-Efficient Air Conditioners of 2022
Best Overall: Lennox XC25
When it comes to energy efficiency in a central air conditioner, the Lennox XC25 is hard to top. Its state-of-the-art technology is what earned this AC the title of EnergyStar’s most efficient model for 2020.
Unlike many other central units, the Lennox XC25 features multiple stages with either a single continuous speed or two speeds, each of which may be adjusted precisely by 1 percent (low and high). Even when the gadget is turned on and off, the temperature can be kept stable. For instance, the XC25’s humidity management features allow for far less noise than competing models (normal regions, dry areas, or coastal).
Runner Up: Amana AVXC20
The AVXC20 from Amana is an energy-efficient, high-quality central air conditioner that is also quite quiet. Special inverter technology allows for power and speed to be automatically adjusted once the thermostat temperature is achieved (so the compressor doesn’t have to work harder than necessary).
The purchase of this item comes with a full warranty. EnergyStar has honored the AVXC20 with the highest level of energy efficiency for the current year.
Best Budget: Keystone KSTAW05CE
The Keystone KSTAW05CE air conditioner, certified by EnergyStar, offers reliable cooling at a reasonable price. In general, more costlier air conditioners have higher energy efficiency ratings. The 5,000 BTU window unit has a remarkably low noise level for its powerful air-conditioning capabilities, and it also has a number of energy-saving options.
The programmable thermostat, LED display, timer, and remote control are all nice touches. As a result of its 12.1 CEER rating, the Keystone has a yearly operating cost of about $40. It’s true that this AC unit is inexpensive, but it’s not a good fit for really large rooms.
Best Portable: Whynter ARC-14SH
Whynter ARC-14SH has a built-in heater, dehumidifier, and fan, making it ideal for individuals who are concerned about their carbon footprint (however, a cooling-only version is available). This 14,000 BTU device features auto drain technology to recycle moisture during the cooling process, making it suitable for cooling spaces up to 500 square feet in size.
Furthermore, it uses R-32 refrigerant, which is 10% more efficient than the standard alternative. Air filters may be easily cleaned when they become clogged with dust or other debris. The Whynter has an exhaust pipe, window kit, and a programmable remote control to help you save energy.
Best for Small Rooms: Frigidaire 6,000 BTU Window-Mounted Air Conditioner FFRE063ZA1
Find an air conditioner that is the right size for the room; more isn’t always better. A larger air conditioner will trap more humidity, making a smaller space feel even drier. The Frigidaire 6,000 BTU Energy Star is an excellent option for spaces between 150 and 250 square feet in size.
This window AC operates on 110 volts, has a remote control, and has a 12.1 EER energy efficiency rating (or the main panel). Additionally, there are three distinct cooling modes, a sleep mode, and a timer that can be set to run for up to 24 hours.
Best Window: LG Electronics 14000 BTU Dual Inverter Window Air Conditioner with Wi-Fi Control
The LG 14,000 BTU window air conditioner’s twin inverter technology earned it a CEER rating of 14. 7, making it up to 25 percent more efficient than the EnergyStar requirements.
In addition to being quite quiet, the unit’s low annual operating cost of $68 is a major plus. A car’s air conditioning system can be controlled via remote, touch screen, or voice utilizing services like Google Assistant or Amazon Alexa, even while driving. LG’s unit uses R32 refrigerant and can cool a space up to 800 square feet in size.
Best for Large Rooms: Senville SENA-24HF/Z Mini Split Air Conditioner
Mini splits are an alternative to central air conditioning; they can be used both to cool and heat a home. Most of the time, they are ductless and simply attach to an exterior wall to act as a heat sink. The SENA-24HF is an excellent micro split with a SEER rating of 20.5, making it suitable for cooling rooms between 1,200 and 1,450 square feet in size. The 24,000 BTU EnergyStar certified unit features heating (for the colder months), dry, and turbo settings.
Last but not least, it works with Google Home and can be operated with a remote or over Wi-Fi. Self-cleaning, in-built dehumidifier, remote-controlled thermostat, and refrigerant leak detector are just some of the features that come standard.
The refrigerant pipe must be run through a wall to reach the indoor air handler, and the HVAC system must be hardwired into the electrical system. If you are not confident in your ability to complete these duties, it is recommended that you obtain an estimate from a certified installer.
FAQs
How much does your electric bill go up with an air conditioner?
Households in Arizona spend an annual average of $400 on cooling their homes. Naturally, larger properties require more robust and costly air conditioners due to the increased cooling load.
Do air conditioners use a lot of electricity?
In terms of energy usage, your home’s air conditioner is likely the biggest culprit. This is notably true in the Southwest United States, where residents regularly turn on their air conditioners regardless of the season.
How much does it cost to run an air conditioner all day?
The cost of operating your air conditioner is based on the number of kilowatt hours it consumes each month. In the United States, one kilowatt-hour of power costs about 12 cents. In addition, the phrase “running your air conditioner all day” may not have the precise meaning you believe it does. Air conditioners can be set to run on cycles as little as 15 minutes, or as often as every two hours. As long as it is large enough, a unit won’t have to be always on for it to fulfill its job.

Conclusion
To cool a room that requires 12000 BTUs, how much power would you need? We determined that the average electricity consumption for a 12000 BTU air conditioner was 900 watts per hour. It would cost us around $1,500 to use it for 8 hours each day, every day, for an entire year. Articles like these might benefit from a discussion of the cost of operating a window air conditioner. No further comment is necessary.
Nguồn: https://spasifikmag.com
Danh mục: Conditioner










